Description
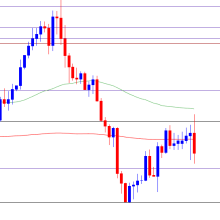
The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) is a popular technical indicator used by traders to identify trends and potential entry and exit points in the Forex market. Unlike a simple moving average, the EMA gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information. Below is a comprehensive EMA strategy that can help you effectively navigate the Forex market.
1. Understanding the EMA
- What is EMA?: The EMA is a type of moving average that places a greater significance on the most recent price data. This makes it more sensitive to price changes and helps traders react quickly to market movements.
- Common EMA Periods: Traders often use different EMA periods, such as the 9, 20, 50, or 200 EMA, depending on their trading style. Shorter EMAs (like the 9 or 20) are used for short-term trades, while longer EMAs (like the 50 or 200) are more suitable for identifying long-term trends.
2. Market Analysis
- Select Currency Pairs: Focus on major currency pairs that exhibit clear trends and sufficient volatility. Pairs like EUR/USD, USD/JPY, and GBP/USD are popular choices due to their liquidity.
- Trend Identification: Use the EMA to determine the market trend. When the price is above the EMA, it indicates a bullish trend, while a price below the EMA indicates a bearish trend.
3. Entry and Exit Points
- EMA Crossovers:
- Bullish Crossover: When a shorter EMA (e.g., 9 EMA) crosses above a longer EMA (e.g., 20 EMA), it generates a buy signal, indicating potential upward momentum.
- Bearish Crossover: When a shorter EMA crosses below a longer EMA, it generates a sell signal, indicating potential downward momentum.
- Price Action Confirmation: Always confirm EMA signals with price action. Look for supporting candlestick patterns (e.g., pin bars, engulfing patterns) to validate your entry points.
- Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit:
- Stop-Loss: Place a stop-loss order slightly below the recent swing low for buy trades or above the recent swing high for sell trades. This helps limit potential losses.
- Take-Profit: Set your take-profit target based on a favorable risk-reward ratio (e.g., 1:2 or 1:3). You can also use previous support and resistance levels to determine exit points.
4. Risk Management
- Position Sizing: Determine your position size based on your risk tolerance and account size. Risk no more than 1-2% of your trading capital on a single trade to protect your account from significant losses.
- Avoid Overleveraging: Use leverage cautiously, as it can amplify both gains and losses. Stick to a comfortable level of leverage that aligns with your risk management strategy.
5. Trading Plan
- Create a Trading Routine: Develop a daily trading plan that outlines your objectives, target currency pairs, and specific strategies to use. Stick to your plan and avoid impulsive decisions.
- Maintain a Trading Journal: Record all your trades, including entry and exit points, reasons for entering, and outcomes. This helps you analyze your performance and refine your strategy over time.
6. Discipline and Patience
- Avoid Overtrading: Focus on high-probability setups rather than forcing trades. Wait for your EMA signals to align with favorable market conditions before entering.
- Emotional Control: Stay disciplined and adhere to your trading plan. Avoid making impulsive decisions based on fear or greed, as these emotions can negatively impact your trading performance.







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.